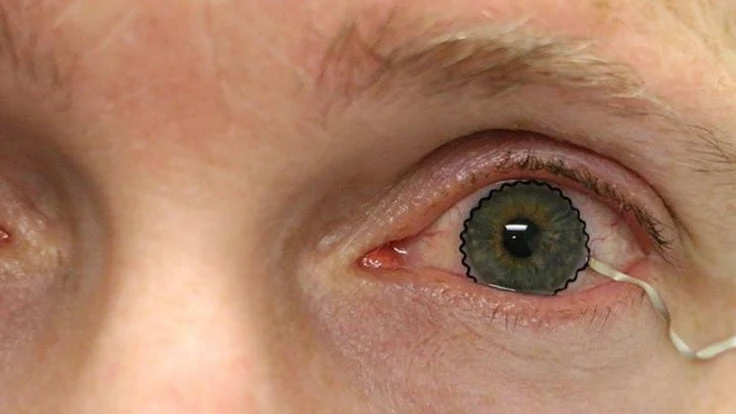
PURDUE UNIVERSITY/CHI HWAN LEE
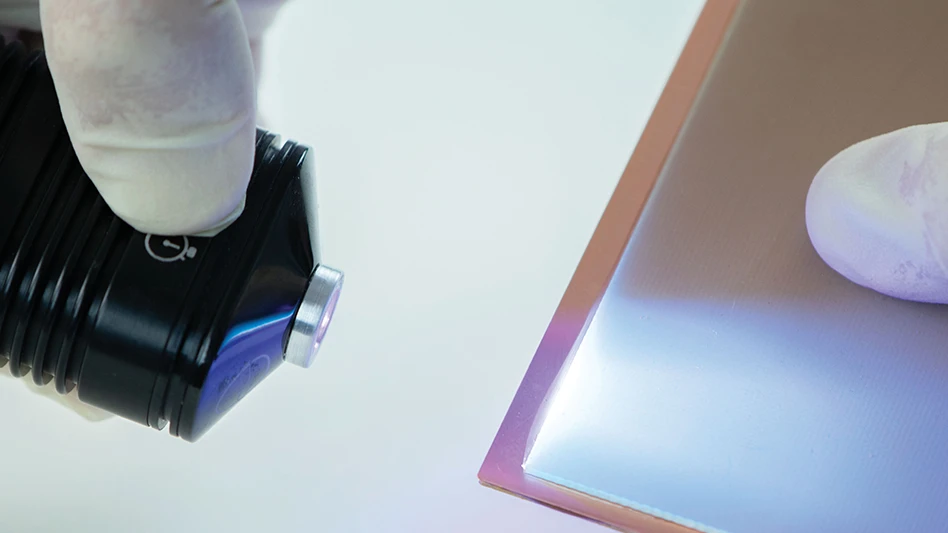
A team of researchers from Purdue University worked with biomedical, mechanical and chemical engineers, along with clinicians, to develop the novel technology. The team enabled commercial soft contact lenses to be a bioinstrumentation tool for unobtrusive monitoring of clinically important information associated with underlying ocular health conditions.
The team's work is published in Nature Communications. The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization helped secure a patent for the technology and it is available for licensing.
"This technology will be greatly beneficial to the painless diagnosis or early detection of many ocular diseases including glaucoma" says Chi Hwan Lee, the Leslie A. Geddes assistant professor of biomedical engineering and assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Purdue who is leading the development team. "Since the first conceptual invention by Leonardo da Vinci, there has been a great desire to utilize contact lenses for eye-wearable biomedical platforms."
Sensors or other electronics previously couldn't be used for commercial soft contact lenses because the fabrication technology required a rigid, planar surface incompatible with the soft, curved shape of a contact lens.
The editors at Today's Medical Developments magazine have covered various developments of contact lens research. Read more here:
https://www.todaysmedicaldevelopments.com/article/medical-device-contact-lens-design-epfl-22515/
https://www.todaysmedicaldevelopments.com/article/drug-dispensing-medical-device-contact-lens-9916/
https://www.todaysmedicaldevelopments.com/article/triggerfish-glaucoma-medical-contact-lens-31816/
https://www.todaysmedicaldevelopments.com/article/bionic-contact-lens-medical-device-design-072913/
The team has paved a unique way that enables the seamless integration of ultrathin, stretchable biosensors with commercial soft contact lenses via wet adhesive bonding. The biosensors embedded on the soft contact lenses record electrophysiological retinal activity from the corneal surface of human eyes, without the need of topical anesthesia that has been required in current clinical settings for pain management and safety.
"This technology will allow doctors and scientists to better understand spontaneous retinal activity with significantly improved accuracy, reliability, and user comfort," says Pete Kollbaum, director of the Borish Center for Ophthalmic Research and an associate professor of optometry at Indiana University who is leading clinical trials.
The other members of the team are Bryan Boudouris, a professor of chemical engineering from Purdue, and Baoxing Xu, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering from the University of Virginia.
This work is funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF CMMI-1928784 & 1928788) and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR FA9550-19-1-0271). For more information about licensing opportunities, contact Patrick Finnerty of OTC at pwfinnery@prf.org.
Latest from Today's Medical Developments
- Copper nanoparticles could reduce infection risk of implanted medical device
- Renishaw's TEMPUS technology, RenAM 500 metal AM system
- #52 - Manufacturing Matters - Fall 2024 Aerospace Industry Outlook with Richard Aboulafia
- Tariffs threaten small business growth, increase costs across industries
- Feed your brain on your lunch break at our upcoming Lunch + Learn!
- Robotics action plan for Europe
- Maximize your First Article Inspection efficiency and accuracy
- UPM Additive rebrands to UPM Advanced





